Cloudy Cloud - Pay As You Go, Upscale As You Need is a blog which tries to take a stab at the Cloud Offerings in three simple steps. As you will walk through this blog you will get to learn more about these steps for choosing the Cloud solution mix that is right for your organization viz., Cloud Service Delivery Methods, Cloud Deployment Methods and Cloud Service Provider.
Knowing Cloud Computing.
Let us start with what is Local Storage and Computing before we jump into the Cloud Computing arena. Local Storage and Computing is when you store data or run programs from your local hard drive and working off the local hard drive is how the computer industry has functioned for decades and some geek's even today advocate that they are better off using local Computing over Cloud Computing. So what is this Cloud Computing and why most of the small scale industries are up for it and a lot of bigger players also are getting into the mix. Cloud Computing in its simplest terms is a way to increase capacity or add capabilities on the fly without investing in brand new infrastructure, training new resources, or licensing new software's. Cloud Computing is any subscription based or pay per use service that extends computer industry's existing capabilities in real time over the Internet. Let's take a deep dive into the three steps I had mentioned at the beginning of the blog to understand Cloud offering.Cloud Service Delivery Methods.
Cloud Computing resources are delivered to users through three basic service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS), they correspond to Hardware, Frameworks, Applications being rented on subscription basis.
In IaaS method of delivering Cloud services, compute resources, complemented by storage and networking capabilities are owned and hosted by a service provider and offered to customers as subscription based or pay per use service or pay as you go service, and the users who manage the infrastructure have full control of the software installation and configuration. E.g. Amazon EC2, MS Azure and Google Compute Engine, etc.
In PaaS model, we have two basic classifications, application Platform as a Service (aPaaS) and integration Platform as a Service (iPaas). In aPaaS, the application development platforms are hosted on Cloud and made available to users over the internet. iPaaS provides a platform for developing and deploying integration's within the cloud and integrating enterprises, application, services with a cloud and also integrating the cloud to another cloud or to the outside world. Users can develop integration flows that connect applications residing in the cloud or on-premises and then deploy them without installing or managing any hardware or middleware. The cost model is again pay-per-use. In this model, the user do not have direct access to the system resources, rather the resource allocation to applications is automatically managed by the platform. E.g. for aPaaS are Google App Engine and Microsoft Azure, etc. E.g. for iPaaS are Dell Bhoomi, mulesoft, Informatica, SAG.
In SaaS model, sometimes referred to as "on-demand software" is a software delivery method that provides access to software and its functions remotely as a Web-based service. Software as a Service allows organizations to access business functionality at a cost typically less than paying for licensed applications as it is subscription based and you typically pay per month or based on usage. E.g. Office 365, Salesforce.com, etc.
Cloud is Cloudy when it comes to 'who is responsible for what' in the Cloud delivery method, it is definitely a big question to answer, the chart below guidelines the breakdown of the responsibilities, violet boxes is what you manage and Oranges are what the service provider do. There is always room for customization.
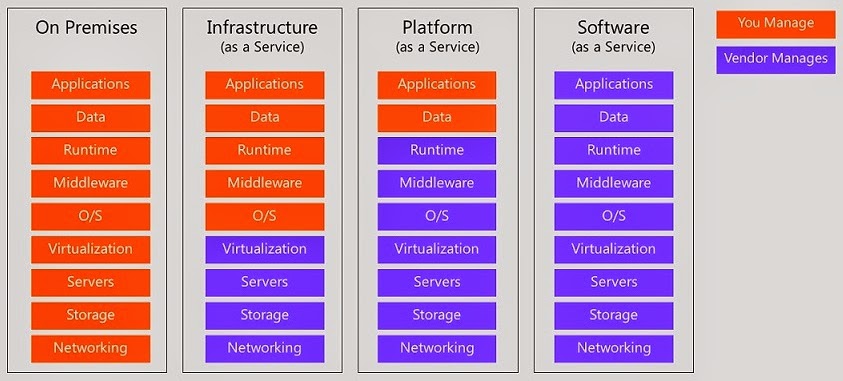
A lot of times the best solution is often a combination of delivery methods. The decisions you make will be based on the applications, frameworks or hardware that best fits the required parameters (budget, time, security, performance, manageability etc.) of your business.
Cloud Deployment Models
Different Cloud deployment models offer varying levels of control, scalability, availability, and cost. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines the four primary models viz., Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Community Cloud and Hybrid Cloud. In Public Cloud Computing the service providers make resources, such as hardware and applications available to the general Public over the Internet, Public Cloud offerings may be free or offered on a pay-per-usage model. In private Cloud Computing model the Cloud infrastructure is hosted, owned and managed internally by the organization it serves. In Community Cloud Computing, Cloud is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that share common interest or concern. Hybrid Cloud Computing is a combination of a Community, Private and Public Clouds in all possible combinations.
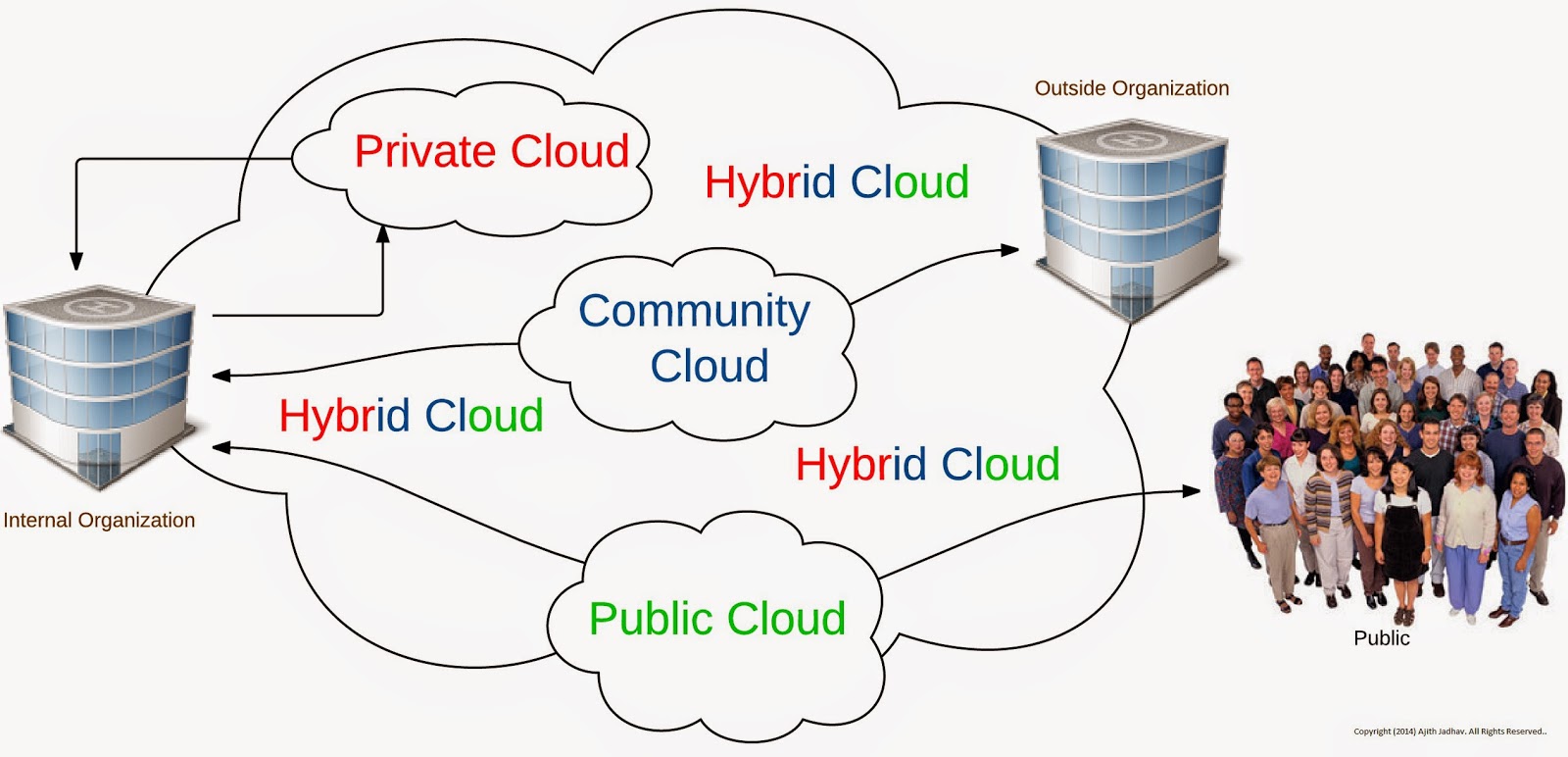
Cloud Deployment Suggestions: The onsite private Cloud is ideal for organizations that require complete control over technology, data and information. Offsite private Clouds offer dynamic scalability of Computing resources, with the highest levels of data security and segmentation. The private Cloud may be a good fit for your organization if you need to meet strict security or compliance requirements, Need robust data segmentation capabilities, Experience fluctuating demand of Computing resources, due to seasonal variation or promotions etc. To summarize, the private Cloud is typically the most expensive of the models to deploy, as it is dedicated solely for one organization and also it provides highest level of data security and segmentation. The Public Cloud is typically the most cost effective of the Cloud Models. It can be deployed quickly and when it comes to economies of scale it is definitely impressive. In the Public Cloud, your organization may sacrifice some control over visibility and data security in exchange for better efficiency. To summarize public cloud computing may not best choice for sensitive or regulated data but definitely a good alternative for greater efficiency and economies of scale. The community Cloud works best when more that one organization share common needs or concern viz., security, compliance requirements, economies of scale etc. The community Cloud provides the advantages of the private Cloud, when it comes to security and advantages of public cloud as multiple organizations partner together, economies of scale are achieved and you have complete control over who you share resources with. Anyways an organization need to be careful when storing private or proprietary data in the Community Cloud, as others may be able to access it. Community Cloud has its own Challenges like allocation of costs, responsibilities, governance and security. The hybrid Cloud combines several Cloud models to create a customized solution based on your business requirements. One could store sensitive information and critical processes in a private Cloud, and less sensitive data and non-critical processes in the Public Cloud. If you need varying levels of security, control, economies of scale and scalability, a hybrid Cloud option is worth considering. In using a mix of various deployment models and various cloud providers the cloud solutions are architected with best practices in mind and ensuring to build and make a completely interoperable could solution.
Choosing the Right Service provider
IaaS Service Providers: The primary evaluation criteria in choosing the IaaS service provider would be Compute, Storage, Network, Security and Access, Service Offerings, Support and Service Levels, Management and DevOps, Price and Billing, the evaluation criteria would be based on you organizational pre-requisites. AWS and Microsoft Azure are clear market leader in the IaaS offerings, google back in 2013 was not visible in the Gartner magic quadrant and now it's listed in the visionaries and it is closing in on the gap, looking at the pace it is inching towards the Leaders quadrant possibly by 2015. Let us looks at comparison between AWS and Azure, you should choose AWS if you require significant scalability, you need to automate a lot, you require local and global availability, you require a robust app marketplace, better security. You should choose Microsoft Azure if you are deeply invested in MS technologies or if you already using Azure PaaS or SaaS(office 365) and want to have single provider, you are ok with scalability limitations, Azure definitely has a better support when compared AWS. | |
Source: Garner webinar on AWS vs Azure
| |
 | |
Gartner Magic Quadrant for IaaS
| |
aPaaS Service Providers: As per Gartner Salesforce is by far the largest provider of the enterprise aPaaS market. Microsoft takes the second place. Google App Engine which stand next to MS has a huge customer base close to 30,000 paying customers, many are small web innovators alongside are few large businesses like Snapchat and Khan Academy. Salesforce is widely used among large businesses. Enterprise customer base is definitely larger that larger than Google, for the reason that Google has limited reputation as an enterprise service provider. A few newer entrants are also doing well like the CloudControl, a German company serving the European market, says it has 400 paying customers for aPaaS and Docker has like 500 paying customers.
 |
Gartner Magic Quadrant for aPaas
|
iPaas Service Providers: Gartner lists Dell Boomi and Informatica on top of its Leaders quadrant, with Boomi having an edge. Just trailing a little low is MuleSoft, the open-source firm that started out supplying a lightweight enterprise service bus for financial customers. We have a few Challengers like Actian and Fujitsu, with Actian having the edge. In the Visionaries quadrant are IBM, SAP, and SnapLogic, with IBM having the edge. And there are many Niche Players.
 |
Gartner Magic Quadrant for iPaaS
|
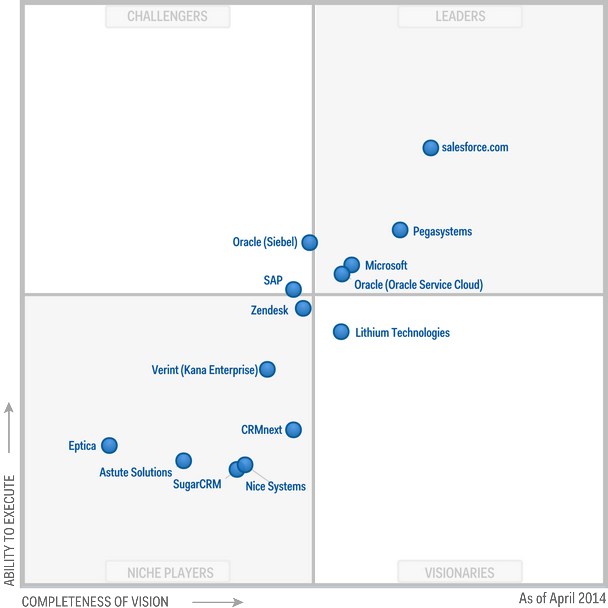 |
Gartner Magic Quadrant for SaaS - CRM
|
References:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/http://aws.amazon.com/
http://www.Cloudproviderusa.com/private-Public-community-or-hybrid-Cloud/
http://www.gartner.com/technology/reprints.do?id=1-1UKQQA6&ct=140528&st=sb
http://www.gartner.com/technology/reprints.do?id=1-1T8MR2K&ct=140417&st=sg
http://www.gartner.com/technology/reprints.do?id=1-1P3OLZW&ct=140107&st=sb
http://www.gartner.com/technology/reprints.do?id=1-1WYKAUG&ct=140711&st=sb
http://www.salesforce.com/CloudComputing/
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/ee309870.aspx
https://www.softwareag.com/corporate/images/sec_SAG_Cloud_Computing_8PG_WP_Sep14-Web_tcm16-122984.pdf
http://www.infoworld.com/article/2683784/Cloud-Computing/what-Cloud-Computing-really-means.html
http://www.planforcloud.com/pages/resources/cloud_services.html
http://blog.cloudharmony.com/2014/07/comparing-cloud-compute-services.html
https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=2&ved=0CEkQFjAB&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.opdion.com%2Fdbimage.php%3Fid%3D552&ei=AEtSVIjUPMueyASjhYHgBw&usg=AFQjCNHxUbdd2vvM3Iz8zgUjGWtUGkGSew&sig2=fpnMoVTyU3nY4ef8XzvqYw&bvm=bv.78597519,d.aWw&cad=rjt
http://www.tomsitpro.com/articles/iaas-providers,1-1560.html
http://www.itworld.com/article/2702083/cloud-computing/paas-winners-and-losers--so-far--might-surprise-you.html






